在分佈式系統中,負載均衡是必不可少的一個模塊,dubbo 中提供了五種負載均衡的實現,在閱讀這塊源碼之前,建議先學習負載均衡的基礎知識。把看源碼當做一個印證自己心中所想的過程,這樣會得到事半功倍的效果
以下源碼分析基於 dubbo 2.77 版本
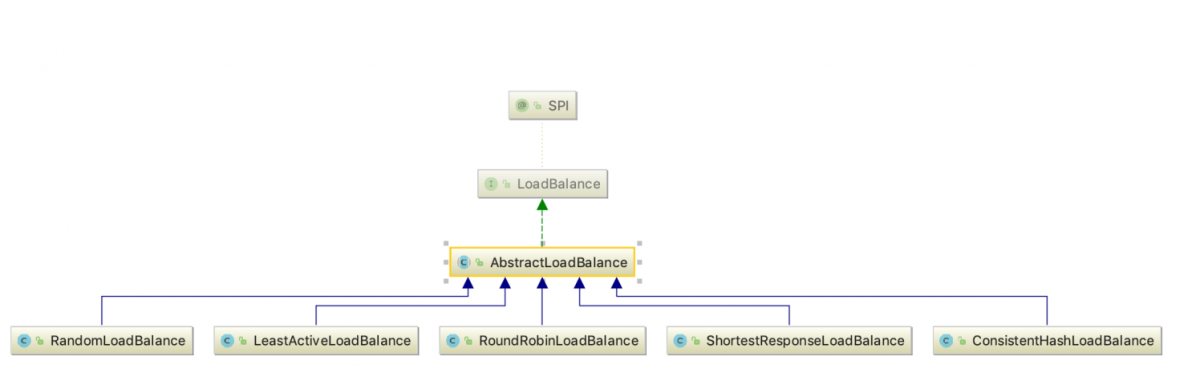
類結構
先來看一下這一塊的類結構圖
大部分算法都是在權重比的基礎上進行負載均衡,RandomLoadBalance 是默認的算法
| 類型 |
描述 |
是否默認 |
是否加權 |
| RandomLoadBalance |
隨機 |
是 |
是,默認權重相同 |
| RoundRobinLoadBalance |
輪訓 |
否 |
是,默認權重相同 |
| LeastActiveLoadBalance |
最少活躍數調用 |
否 |
不完全是,默認權重相同,僅在活躍數相同時按照權重比隨機 |
| ConsistentHashLoadBalance |
一致性hash |
否 |
否 |
| ShortestResponseLoadBalance |
最短時間調用 |
否 |
不完全是,默認權重相同,僅在預估調用相同時按照權重比隨機 |
AbstractLoadBalance
AbstractLoadBalance 對一些通用的操作做了處理,是一個典型的模板方法模式的實現
select 方法只做一些簡單的範圍校驗,具體的實現有子類通過 doSelect 方法去實現
@Override
public <T> Invoker<T> select(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(invokers)) {
return null;
}
if (invokers.size() == 1) {
return invokers.get(0);
}
return doSelect(invokers, url, invocation);
}
getWeight方法封裝了獲取一個調用者的權重值的方法,並加入了預熱處理
int getWeight(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) {
int weight;
URL url = invoker.getUrl();
// Multiple registry scenario, load balance among multiple registries.
// 註冊中心不需要預熱
if (REGISTRY_SERVICE_REFERENCE_PATH.equals(url.getServiceInterface())) {
weight = url.getParameter(REGISTRY_KEY + "." + WEIGHT_KEY, DEFAULT_WEIGHT);
} else {
// 獲取配置的權重值
weight = url.getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(), WEIGHT_KEY, DEFAULT_WEIGHT);
if (weight > 0) {
// 獲取服務提供者啟動時的時間戳
long timestamp = invoker.getUrl().getParameter(TIMESTAMP_KEY, 0L);
if (timestamp > 0L) {
// 獲取啟動時長
long uptime = System.currentTimeMillis() - timestamp;
// 當前時間小於服務提供者啟動時間,直接給一個最小權重1
if (uptime < 0) {
return 1;
}
// 獲取預熱時間
int warmup = invoker.getUrl().getParameter(WARMUP_KEY, DEFAULT_WARMUP);
// 如果小於預熱時間,計算權重
if (uptime > 0 && uptime < warmup) {
weight = calculateWarmupWeight((int)uptime, warmup, weight);
}
}
}
}
// 取與零比較的最大值,保證不會出現負值權重
return Math.max(weight, 0);
}
calculateWarmupWeight 方法用來計算權重,保證隨着預熱時間的增加,權重逐漸達到設置的權重
static int calculateWarmupWeight(int uptime, int warmup, int weight) {
// 運行時間/(預熱時間/權重)
int ww = (int) ( uptime / ((float) warmup / weight));
// 保證計算的權重最小值是1,並且不能超過設置的權重
return ww < 1 ? 1 : (Math.min(ww, weight));
}
RandomLoadBalance
隨機調用是負載均衡算法中最常用的算法之一,也是 dubbo 的默認負載均衡算法,實現起來也較為簡單
隨機調用的缺點是在調用量比較少的情況下,有可能出現不均勻的情況
@Override
protected <T> Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
// Number of invokers
int length = invokers.size();
// Every invoker has the same weight?
boolean sameWeight = true;
// the weight of every invokers
int[] weights = new int[length];
// the first invoker's weight
int firstWeight = getWeight(invokers.get(0), invocation);
weights[0] = firstWeight;
// The sum of weights
int totalWeight = firstWeight;
for (int i = 1; i < length; i++) {
int weight = getWeight(invokers.get(i), invocation);
// save for later use
// 依次把權重放到數組對應的位置
weights[i] = weight;
// Sum
// 累加權重
totalWeight += weight;
// 如果出現權重不一樣的,sameWeight 設為false
if (sameWeight && weight != firstWeight) {
sameWeight = false;
}
}
if (totalWeight > 0 && !sameWeight) {
// If (not every invoker has the same weight & at least one invoker's weight>0), select randomly based on totalWeight.
// 在總權重裏面隨機選擇一個偏移量
int offset = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(totalWeight);
// Return a invoker based on the random value.
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
offset -= weights[i];
// 依次用偏移量減去當前權重,小於0說明選中
if (offset < 0) {
return invokers.get(i);
}
}
}
// If all invokers have the same weight value or totalWeight=0, return evenly.
// 如果所有的調用者有同樣的權重或者總權重為0,則隨機選擇一個
return invokers.get(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(length));
}
RoundRobinLoadBalance
輪訓算法避免了隨機算法在小數據量產生的不均勻問題,我個人認為,輪訓算法可以理解為隨機算法的一種特例,在大量請求的情況下,從調用次數看,和隨機並無區別,主要區別在於短時間內的調用分配上
加權輪訓算法給人的直觀感受,實現起來並不複雜,算出一權重總量,依次調用即可
例如A,B,C 三個節點的權重比依次 1,200,1000,如果依次輪訓調用,就會出現先調用A 10 次,再調用B 200次,最後調用 C 1000次,不斷重複前面的過程
但這樣有一個問題,我們可以發現C 被練習調用1000次,會對C瞬間造成很大的壓力
dubbo的新版本採用的是平滑加權輪詢算法,輪訓的過程中節點之間穿插調用,可以避免了上面說的問題,因此這塊源碼看起來會稍有難度
輪訓算法 在dubbo 在升級的過程中,做過多次優化,有興趣的可以去了解下該算法的優化過程,也是件很有意思的事情
public class RoundRobinLoadBalance extends AbstractLoadBalance {
public static final String NAME = "roundrobin";
private static final int RECYCLE_PERIOD = 60000;
protected static class WeightedRoundRobin {
// 權重值
private int weight;
// 當前權重值
private AtomicLong current = new AtomicLong(0);
// 最後一次使用該對象時間
private long lastUpdate;
public int getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public void setWeight(int weight) {
this.weight = weight;
current.set(0);
}
// 獲取自增權重基數的當前權重值
public long increaseCurrent() {
return current.addAndGet(weight);
}
public void sel(int total) {
current.addAndGet(-1 * total);
}
public long getLastUpdate() {
return lastUpdate;
}
// 設置最後一次更新時間戳
public void setLastUpdate(long lastUpdate) {
this.lastUpdate = lastUpdate;
}
}
private ConcurrentMap<String, ConcurrentMap<String, WeightedRoundRobin>> methodWeightMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, ConcurrentMap<String, WeightedRoundRobin>>();
/**
* get invoker addr list cached for specified invocation
* <p>
* <b>for unit test only</b>
*
* @param invokers
* @param invocation
* @return
*/
protected <T> Collection<String> getInvokerAddrList(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, Invocation invocation) {
String key = invokers.get(0).getUrl().getServiceKey() + "." + invocation.getMethodName();
Map<String, WeightedRoundRobin> map = methodWeightMap.get(key);
if (map != null) {
return map.keySet();
}
return null;
}
@Override
protected <T> Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
// {group}/{interfaceName}:{version} + methoName 獲取當前消費者的唯一標示
String key = invokers.get(0).getUrl().getServiceKey() + "." + invocation.getMethodName();
// 獲取對應的 WeightedRoundRobin map,如果不存在,new 一個map放進去
ConcurrentMap<String, WeightedRoundRobin> map = methodWeightMap.computeIfAbsent(key, k -> new ConcurrentHashMap<>());
int totalWeight = 0;
long maxCurrent = Long.MIN_VALUE;
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
Invoker<T> selectedInvoker = null;
WeightedRoundRobin selectedWRR = null;
for (Invoker<T> invoker : invokers) {
// 服務提供者在的唯一標識
String identifyString = invoker.getUrl().toIdentityString();
int weight = getWeight(invoker, invocation);
WeightedRoundRobin weightedRoundRobin = map.computeIfAbsent(identifyString, k -> {
WeightedRoundRobin wrr = new WeightedRoundRobin();
wrr.setWeight(weight);
return wrr;
});
// 如果權重改變了,更新 weightedRoundRobin 裏面權重的值
if (weight != weightedRoundRobin.getWeight()) {
//weight changed
weightedRoundRobin.setWeight(weight);
}
// 當前權重自增自身權重
long cur = weightedRoundRobin.increaseCurrent();
// 設置最後一次更新時間戳
weightedRoundRobin.setLastUpdate(now);
// 如果當前權重大於最大當前權重
if (cur > maxCurrent) {
// 重置最大當前權重的值
maxCurrent = cur;
// 把當前提供者設為選中的提供者
selectedInvoker = invoker;
// 把當前輪訓權重實例設為選中
selectedWRR = weightedRoundRobin;
}
// 累計總權重
totalWeight += weight;
}
// 提供者有變化
if (invokers.size() != map.size()) {
// 超過60s沒有使用,刪除掉
map.entrySet().removeIf(item -> now - item.getValue().getLastUpdate() > RECYCLE_PERIOD);
}
if (selectedInvoker != null) {
// 減去總權重
// 關於這個地方為什麼要減去總權重,是一個很容易造成迷惑的地方
// 我的理解:每一次調用循環 每個提供者的 當前權重 都會自增自己的權重
// 因此在選中后(只有一個被選中),再減去總權重,正好保證了所有 WeightedRoundRobin 中當前權重之和永遠等於0
selectedWRR.sel(totalWeight);
return selectedInvoker;
}
// 理論上不會走到這個地方
// should not happen here
return invokers.get(0);
}
}
LeastActiveLoadBalance
最少活躍數調用算法是指在調用時判斷此時每個服務提供者此時正在處理的請求個數,選取最小的調用
dubbo 在實現該算法時的具體邏輯如下
- 選取所有活躍數最少的提供者
- 如果只有一個,直接返回
- 如果權重不同,加權隨機選擇一個
- 如果權重相同,隨機選擇一個
@Override
protected <T> Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
// Number of invokers
int length = invokers.size();
// The least active value of all invokers
// 最少活躍數量
int leastActive = -1;
// The number of invokers having the same least active value (leastActive)
// 有同樣活躍值的提供者數量
int leastCount = 0;
// The index of invokers having the same least active value (leastActive)
int[] leastIndexes = new int[length];
// the weight of every invokers
// 每一個提供者的權重
int[] weights = new int[length];
// The sum of the warmup weights of all the least active invokers
// 最少活躍提供者的總權重
int totalWeight = 0;
// The weight of the first least active invoker
int firstWeight = 0;
// Every least active invoker has the same weight value?
// 所有的最少活躍提供者是否擁有同樣的權重值
boolean sameWeight = true;
// Filter out all the least active invokers
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
Invoker<T> invoker = invokers.get(i);
// Get the active number of the invoker
// 活躍數量
int active = RpcStatus.getStatus(invoker.getUrl(), invocation.getMethodName()).getActive();
// Get the weight of the invoker's configuration. The default value is 100.
// 獲取權重值
int afterWarmup = getWeight(invoker, invocation);
// save for later use
// 保存權重留着後面用
weights[i] = afterWarmup;
// If it is the first invoker or the active number of the invoker is less than the current least active number
// 如果是第一個提供者,或者當前活躍數量比最少的少
if (leastActive == -1 || active < leastActive) {
// Reset the active number of the current invoker to the least active number
// 重置最少活躍數量
leastActive = active;
// Reset the number of least active invokers
// 重置最少活躍提供者的數量
leastCount = 1;
// Put the first least active invoker first in leastIndexes
// 把最少活躍提供者的索引保存起來
leastIndexes[0] = i;
// Reset totalWeight
// 重置總權重
totalWeight = afterWarmup;
// Record the weight the first least active invoker
// 記錄第一個最少活躍提供者的權重
firstWeight = afterWarmup;
// Each invoke has the same weight (only one invoker here)
// 每個最少活躍提供者是否有同樣的權重???
sameWeight = true;
// If current invoker's active value equals with leaseActive, then accumulating.
// 如果當前活躍數量等於最少活躍數量
} else if (active == leastActive) {
// Record the index of the least active invoker in leastIndexes order
// 最少活躍提供者的索引依次放入 leastIndexes
leastIndexes[leastCount++] = i;
// Accumulate the total weight of the least active invoker
// 累計最少活躍提供者的總權重
totalWeight += afterWarmup;
// If every invoker has the same weight?
// 如果當前權重和第一個最少活躍的權重不同,sameWeight 設為false
if (sameWeight && afterWarmup != firstWeight) {
sameWeight = false;
}
}
}
// Choose an invoker from all the least active invokers
// 最少活躍提供者只有一個,直接返回
if (leastCount == 1) {
// If we got exactly one invoker having the least active value, return this invoker directly.
return invokers.get(leastIndexes[0]);
}
// 如擁有不同的權重,在權重的基礎上隨機選取一個,可以參考 RandomLoadBalance,有同樣的寫法
if (!sameWeight && totalWeight > 0) {
// If (not every invoker has the same weight & at least one invoker's weight>0), select randomly based on
// totalWeight.
int offsetWeight = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(totalWeight);
// Return a invoker based on the random value.
for (int i = 0; i < leastCount; i++) {
int leastIndex = leastIndexes[i];
offsetWeight -= weights[leastIndex];
if (offsetWeight < 0) {
return invokers.get(leastIndex);
}
}
}
// 權重相同,隨機選取一個
// If all invokers have the same weight value or totalWeight=0, return evenly.
return invokers.get(leastIndexes[ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(leastCount)]);
}
ShortestResponseLoadBalance
最短時間調用調用算法是指預估出來每個處理完請求的提供者所需時間,然後又選擇最少最短時間的提供者進行調用,整體處理邏輯和最少活躍數算法基本相似
dubbo 在實現該算法時的具體邏輯如下
- 選取所有預估處理時間最短的提供者
- 如果只有一個,直接返回
- 如果權重不同,加權隨機選擇一個
- 如果權重相同,隨機選擇一個
@Override
protected <T> Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
// Number of invokers
int length = invokers.size();
// Estimated shortest response time of all invokers
// 最少響應時間
long shortestResponse = Long.MAX_VALUE;
// The number of invokers having the same estimated shortest response time
// 最少響應時間的提供者數量
int shortestCount = 0;
// The index of invokers having the same estimated shortest response time
int[] shortestIndexes = new int[length];
// the weight of every invokers
int[] weights = new int[length];
// The sum of the warmup weights of all the shortest response invokers
// 最少響應時間的提供者的總權重
int totalWeight = 0;
// The weight of the first shortest response invokers
// 第一個最少響應時間的權重
int firstWeight = 0;
// Every shortest response invoker has the same weight value?
// 所有的最少響應時間提供者是否擁有同樣的權重值
boolean sameWeight = true;
// Filter out all the shortest response invokers
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
Invoker<T> invoker = invokers.get(i);
RpcStatus rpcStatus = RpcStatus.getStatus(invoker.getUrl(), invocation.getMethodName());
// Calculate the estimated response time from the product of active connections and succeeded average elapsed time.
// 平均響應成功時間
long succeededAverageElapsed = rpcStatus.getSucceededAverageElapsed();
// 活躍的連接連接數量
int active = rpcStatus.getActive();
// 預估響應時間
long estimateResponse = succeededAverageElapsed * active;
// 獲取權重值
int afterWarmup = getWeight(invoker, invocation);
// 保存權重留着後面用
weights[i] = afterWarmup;
// Same as LeastActiveLoadBalance
// 如果預估時間小於最少的響應時間
if (estimateResponse < shortestResponse) {
// 重置最少響應時間
shortestResponse = estimateResponse;
// 最少響應時間的提供者數量設為1
shortestCount = 1;
// 保存提供者下標
shortestIndexes[0] = i;
// 重置最少響應時間的提供者的總權重
totalWeight = afterWarmup;
// 重置第一個最少響應時間的權重
firstWeight = afterWarmup;
sameWeight = true;
// 如果當前最少響應時間等於最少響應時間
} else if (estimateResponse == shortestResponse) {
// 最少最少響應時間的下標依次放入 shortestIndexes
shortestIndexes[shortestCount++] = i;
// 累計最少響應時間的總權重
totalWeight += afterWarmup;
// 如果當前權重和第一個最少響應時間的權重不同,sameWeight 設為false
if (sameWeight && i > 0
&& afterWarmup != firstWeight) {
sameWeight = false;
}
}
}
// 最少最少響應時間只有一個,直接返回
if (shortestCount == 1) {
return invokers.get(shortestIndexes[0]);
}
// 如擁有不同的權重,在權重的基礎上隨機選取一個,可以參考 RandomLoadBalance,有同樣的寫法
if (!sameWeight && totalWeight > 0) {
int offsetWeight = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(totalWeight);
for (int i = 0; i < shortestCount; i++) {
int shortestIndex = shortestIndexes[i];
offsetWeight -= weights[shortestIndex];
if (offsetWeight < 0) {
return invokers.get(shortestIndex);
}
}
}
// 權重相同,隨機選取一個
return invokers.get(shortestIndexes[ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(shortestCount)]);
}
ConsistentHashLoadBalance
一致性hash算法是一種廣泛應用與分佈式緩存中的算法,該算法的優勢在於新增和刪除節點后,只有少量請求發生變動,大部分請求仍舊映射到原來的節點
為了防止節點過少,造成節點分佈不均勻,一般採用虛擬節點的方式,dubbo默認的是160個虛擬節點
網上關於一致性hash算法的文章有很多,這裏就不再多贅述,以下是dubbo中的實現,需要說明的是, 一致性hash算法中權重配置不起作用
@Override
protected <T> Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
String methodName = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation);
// {group}/{interfaceName}:{version} + methoName 獲取當前消費者的唯一標示
String key = invokers.get(0).getUrl().getServiceKey() + "." + methodName;
// using the hashcode of list to compute the hash only pay attention to the elements in the list
int invokersHashCode = invokers.hashCode();
// 獲取當前消費者的一致性hash選擇器
ConsistentHashSelector<T> selector = (ConsistentHashSelector<T>) selectors.get(key);
// 如果 selector 還沒初始化,或者 invokers 已經變化,重新初始化 selector
if (selector == null || selector.identityHashCode != invokersHashCode) {
selectors.put(key, new ConsistentHashSelector<T>(invokers, methodName, invokersHashCode));
selector = (ConsistentHashSelector<T>) selectors.get(key);
}
return selector.select(invocation);
}
// 一致性hash選擇器
private static final class ConsistentHashSelector<T> {
// 存儲hash環的數據結構 節點 -> 提供者
private final TreeMap<Long, Invoker<T>> virtualInvokers;
// 虛擬節點數量
private final int replicaNumber;
// 用來標示所有提供者是唯一標示
private final int identityHashCode;
// 用來存儲計算hash值參數下標的數組,例如計算第一個和第三個參數 該數組為[0,2]
private final int[] argumentIndex;
ConsistentHashSelector(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, String methodName, int identityHashCode) {
this.virtualInvokers = new TreeMap<Long, Invoker<T>>();
this.identityHashCode = identityHashCode;
URL url = invokers.get(0).getUrl();
// 虛擬節點數量,默認 160
this.replicaNumber = url.getMethodParameter(methodName, HASH_NODES, 160);
// 默認只對第一個參數進行hash
String[] index = COMMA_SPLIT_PATTERN.split(url.getMethodParameter(methodName, HASH_ARGUMENTS, "0"));
argumentIndex = new int[index.length];
for (int i = 0; i < index.length; i++) {
argumentIndex[i] = Integer.parseInt(index[i]);
}
for (Invoker<T> invoker : invokers) {
String address = invoker.getUrl().getAddress();
// 關於這個地方為什麼要除以4,我理解的是md5後為16字節的數組,計算hash值只需要用到四個字節,所以可以用四次
// 因此除以4,算是一個性能優化點
for (int i = 0; i < replicaNumber / 4; i++) {
// md5, 獲得一個長度為16的字節數組
byte[] digest = md5(address + i);
for (int h = 0; h < 4; h++) {
// 如果h=0,則用第0,1,2,3四個字節進行位運算,得出一個0-2^32-1的值
// 如果h=1,則用第4,5,6,7四個字節進行位運算,得出一個0-2^32-1的值
// 如果h=2,則用第8,9,10,11四個字節進行位運算,得出一個0-2^32-1的值
// 如果h=3,則用第12,13,14,15四個字節進行位運算,得出一個0-2^32-1的值
long m = hash(digest, h);
virtualInvokers.put(m, invoker);
}
}
}
}
public Invoker<T> select(Invocation invocation) {
String key = toKey(invocation.getArguments());
byte[] digest = md5(key);
return selectForKey(hash(digest, 0));
}
// 根據配置生成計算hash值的key
private String toKey(Object[] args) {
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder();
for (int i : argumentIndex) {
if (i >= 0 && i < args.length) {
buf.append(args[i]);
}
}
return buf.toString();
}
private Invoker<T> selectForKey(long hash) {
// 找到hash值在hash環上的位置
// ceilingEntry 方法返回大於或者等於當前key的鍵值對
Map.Entry<Long, Invoker<T>> entry = virtualInvokers.ceilingEntry(hash);
// 如果返回為空,說明落在了hash環中2的32次方-1的最後,直接返回第一個
if (entry == null) {
entry = virtualInvokers.firstEntry();
}
return entry.getValue();
}
// 得出一個0-2^32-1的值, 四個字節組成一個長度為32位的二進制数字並轉化為long值
private long hash(byte[] digest, int number) {
return (((long) (digest[3 + number * 4] & 0xFF) << 24)
| ((long) (digest[2 + number * 4] & 0xFF) << 16)
| ((long) (digest[1 + number * 4] & 0xFF) << 8)
| (digest[number * 4] & 0xFF))
& 0xFFFFFFFFL;
}
private byte[] md5(String value) {
MessageDigest md5;
try {
md5 = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5");
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(), e);
}
md5.reset();
byte[] bytes = value.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
md5.update(bytes);
return md5.digest();
}
}
總結
以上就是dubbo負載均衡源碼的全部解析,如果還是不明白,可以看下官方文檔的解析
http://dubbo.apache.org/zh-cn/docs/source_code_guide/loadbalance.html
dubbo的負載均衡算法總體來說並不複雜,代碼寫的也很優雅,簡潔,看起來很舒服,而且有很多細節的處理值得稱讚,例如預熱處理,輪訓算法的平滑處理等。
我們平時使用時,可以根據自己的業務場景,選擇適合自己的算法,當然,一般情況下,默認的的隨機算法就能滿足我們的日常需求,而且隨機算法的性能足夠好。
如果覺得dubbo提供的五種算法都不能滿足自己的需求,還可以通過dubbo的SPI機制很方便的擴展自己的負載均衡算法。
本站聲明:網站內容來源於博客園,如有侵權,請聯繫我們,我們將及時處理
【其他文章推薦】
※台北網頁設計公司這麼多,該如何挑選?? 網頁設計報價省錢懶人包"嚨底家"
※網頁設計公司推薦更多不同的設計風格,搶佔消費者視覺第一線
※想知道購買電動車哪裡補助最多?台中電動車補助資訊懶人包彙整
※南投搬家費用,距離,噸數怎麼算?達人教你簡易估價知識!
※教你寫出一流的銷售文案?